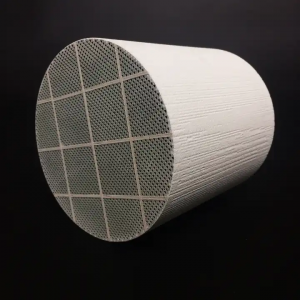
Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) is an advanced device used to reduce particulate matter emissions in diesel engine exhaust. It plays an important role in environmental protection and health, greatly reducing the impact of harmful particulate matter produced by diesel vehicles on the air and human health.
Particulate matter is an important pollutant in diesel engine exhaust and consists of fine particles produced during the combustion process, including carbon, sulfur, metals and other organic matter. The diameter of these particles usually ranges from 0.1 to 10 microns and can penetrate deep into the human respiratory system, posing a serious threat to health. Therefore, reducing particulate matter emissions is particularly important.
The working principle of DPF is mainly based on two processes: physical filtration and regeneration cleaning. Physical filtration refers to capturing the particulate matter in the exhaust gas through a precise ceramic or metal filter element, while allowing the exhaust gas to pass smoothly. The pore structure on these filters effectively blocks particulate matter but allows exhaust gases to flow through. The captured particles will accumulate on the surface of the filter element to form a layer of ash.
Over time, more and more particulate matter accumulates on the filter element, which increases the exhaust resistance of the exhaust gas and reduces engine performance. In order to maintain normal operation and clean the filter element, DPF also uses regenerative cleaning technology. Regenerative cleaning includes two methods: passive regeneration and active regeneration.
Passive regeneration refers to the process in which high-temperature exhaust gas flows through the filter element to burn accumulated particulate matter. When the temperature reaches a certain threshold, the particulate matter on the filter element will undergo an oxidation reaction and be converted into carbon dioxide and water vapor, thereby purifying the filter element and restoring its filtration efficiency.
Active regeneration refers to raising the temperature of the filter element through controllable methods, such as adding regenerant or increasing the exhaust gas temperature, and promotes the oxidation reaction of particulate matter. The active regeneration method is more reliable and can clean and restore the filter element at a lower temperature.
The filter element of DPF is a key component. It consists of a series of small channels, which are similar to screens and can filter out most particulate matter. At the same time, the surface of the filter element is also coated with a catalyst for chemical reactions. When the exhaust gas passes through the DPF, the particulate matter is captured by the filter element and adheres to the channel wall; nitrogen oxides and organic matter are converted through chemical reactions under the action of the catalyst. As particulate matter accumulates on the surface of the filter element, the permeability of the filter element gradually decreases, and the reaction effect will also be affected. Therefore, in order to keep the DPF working efficiently, it is necessary to replace or clean the filter element regularly.
The use of DPF can not only reduce particulate matter emissions, but also improve the combustion efficiency and power output of diesel engines. Since the accumulation of particulate matter will increase exhaust resistance, using DPF can reduce this resistance and improve engine efficiency and fuel utilization. In addition, DPF can also reduce the emission of black smoke from the vehicle’s exhaust during the startup process, improving driving stability and comfort.
However, there are also some problems in the application of DPF. First of all, the filter element will gradually lose its filtration function due to the accumulation of particulate matter, and needs to be cleaned or replaced regularly. Secondly, changes in fuel quality, such as increased sulfur content or the use of inferior diesel, can lead to clogging and damage to the filter element. In addition, the cleaning and regeneration process of DPF will produce a certain amount of energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions, and its impact on the environment and resources cannot be ignored.
In summary, DPF, as an important technology for reducing particulate matter emissions from diesel vehicles, can efficiently filter and purify particulate matter in exhaust gas, playing a positive role in improving air quality and protecting human health. With the continuous advancement of technology and the promotion of applications, DPF will be able to achieve higher filtration efficiency and more sustainable cleaning methods, contributing to the continuous improvement and sustainable development of the environment.
Post time: Dec-04-2023